Estimation of Gaussian graphical model with multipartite blockwise latent structure
janine_MBM.RmdGenerating Gaussian data from a Graphical Model with Multipartite SBM structure
We use the packages GREMLIN and rggm to draw hopefully realistic Gaussian multivariate data faithful to the graphical model of an underlying multipartite stochastic bloc model (MBM).
We first set some parameters to define an MBM with two partition:
## Two partition of nodes v_nNodes <- c(60, 40) ## Proporitions of blocks in each partition v_blockProp <- list(c(1/3, 1/3, 1/3), c(.6,.4)) # group proportions v_nBlocks <- c(3, 2) ## Multipartite architecture ## - adjacency matrices for the "intra" interactions: c(1,1), c(2,2) ## - 1 incidence matrice for the "intra" interactions: c(1,2) architecture <- rbind(c(1,1), c(1,2), c(2,2)) interactions <- c("adj", "inc", "adj") ## The probabilities of connection are defined inter and intra partitions p11 <- diag(.4, v_nBlocks[[1]]) + 0.01 # connectivity matrix: affiliation network p22 <- diag(.4, v_nBlocks[[2]]) + 0.01 # connectivity matrix: affiliation network p12 <- matrix(0.01, v_nBlocks[[1]], v_nBlocks[[2]]) p12[1, 1] <- p12[3, 2] <- .2 connectParam <- rbind(cbind(p11, p12), cbind(t(p12), p22))
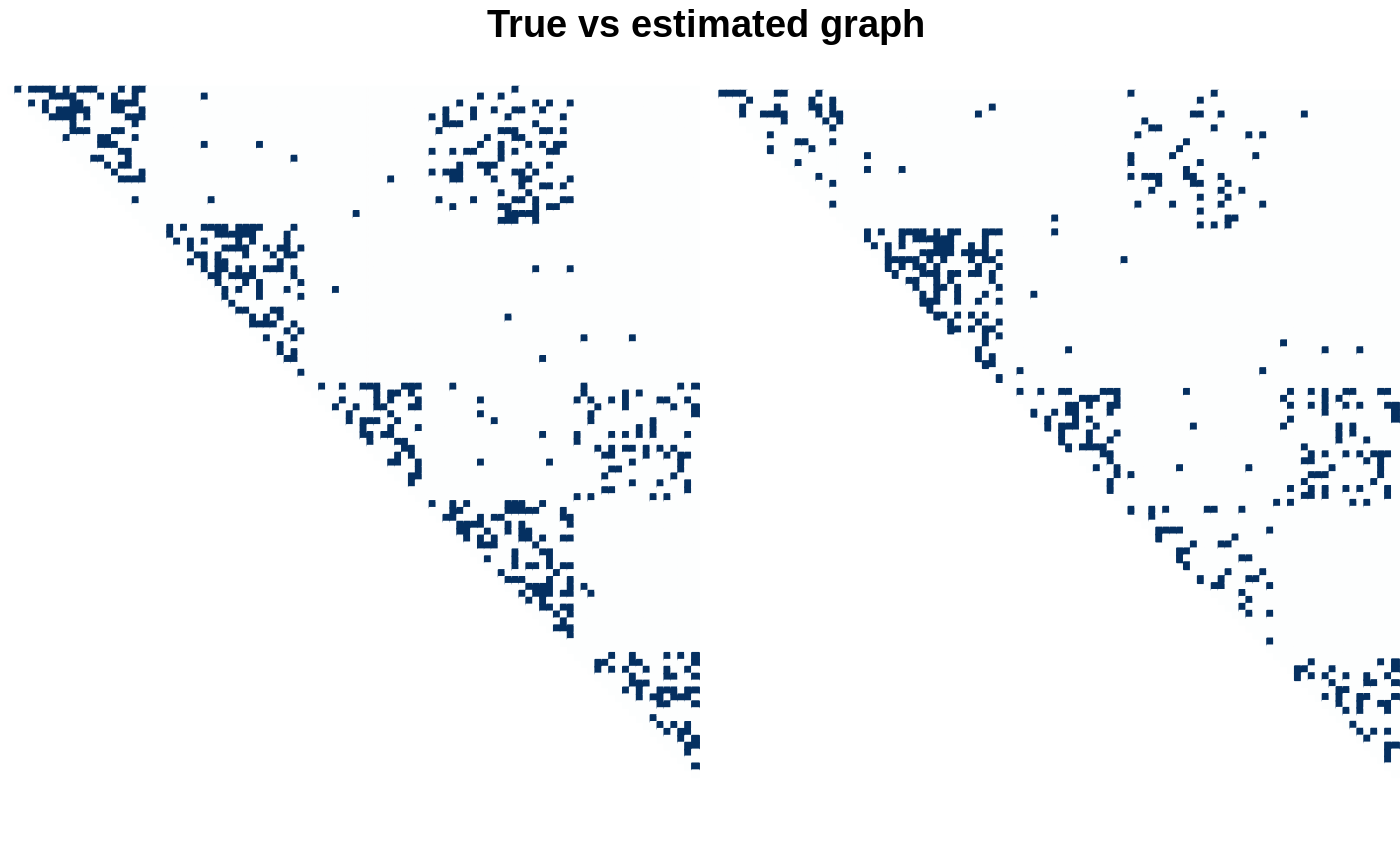
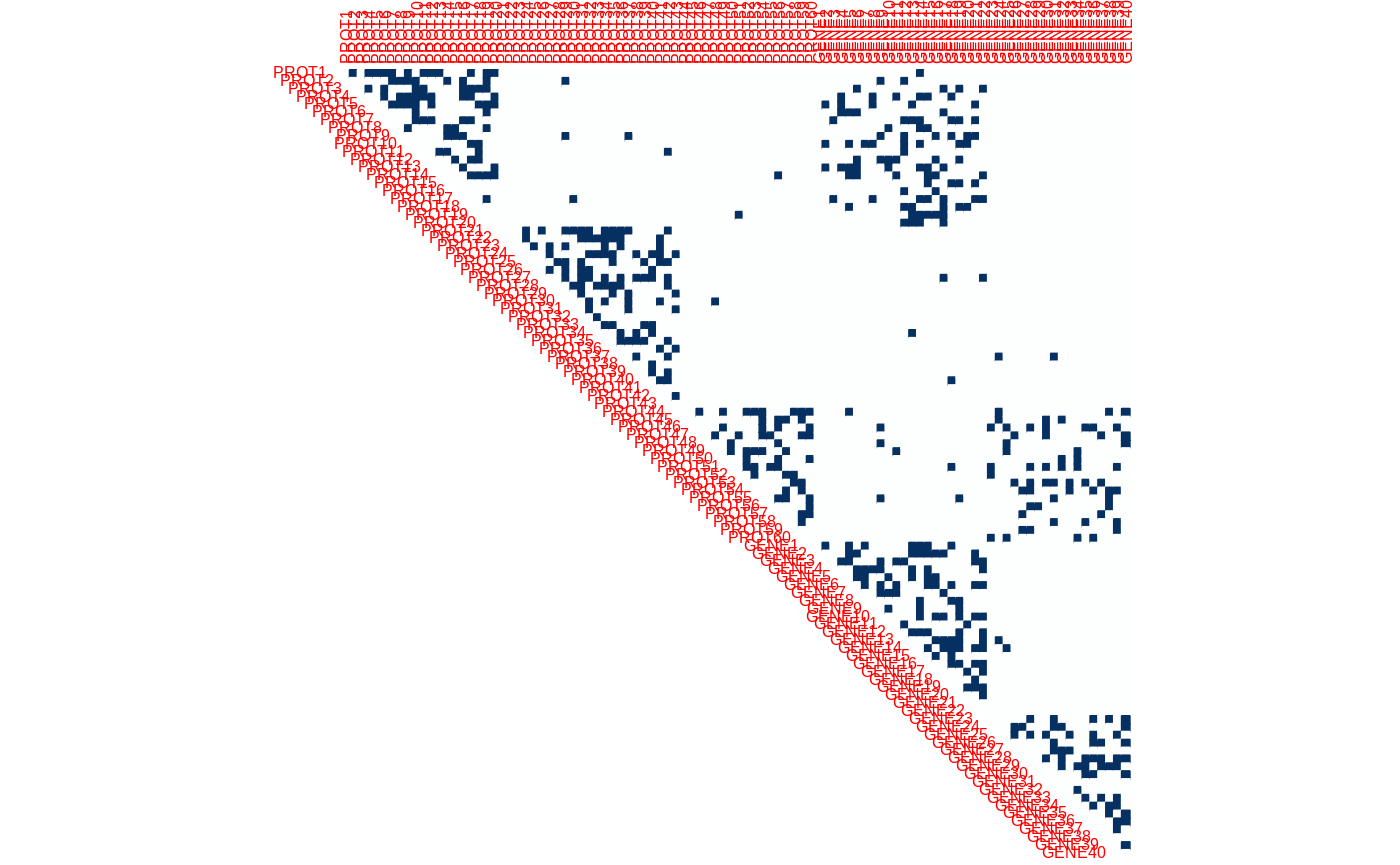
The network itself is then sampled: - the first partition (“proteins”) exhibits 3 blocks (intra-protein connections); - the second partition (“genes”) exhibits two blocks (intra-gene connections); - and there are two blocks of connections (inter protein-gene connection) between block 1 of proteins and block 1 of genes, and block 3 of proteins and block 2 of genes.
size_partitioned <- function(nbNodes, blockProp) stats::rmultinom(1, nbNodes, blockProp) sizes <- unlist(mapply(size_partitioned, v_nNodes, v_blockProp)) myMBM <- igraph::sample_sbm(sum(v_nNodes), connectParam, sizes) myMBM <- igraph::set_vertex_attr(myMBM, "memberships", value = rep(1:length(sizes), sizes)) myMBM <- igraph::set_vertex_attr(myMBM, "partition", value = rep(c("protein", "gene"), v_nNodes)) myMBM <- igraph::set_vertex_attr(myMBM, "name", value = c(paste0("PROT", 1:v_nNodes[1]), paste0("GENE", 1:v_nNodes[2]))) corrplot(as_adj(myMBM, sparse = FALSE), method = "color", is.corr=FALSE, tl.cex = .5, cl.pos = "n", type = "upper")
From this network we build a signed precision matrix
Omega <- graph2prec(myMBM, cond_var = rep(1, sum(v_nNodes)), neg_prop = 0.5) Sigma <- solve(Omega)
We can finally sample some multivariate Gaussian data.
n <- 500 means <- rep(0, sum(v_nNodes)) X <- rmgaussian(n, means, Sigma)
Network Inference with Janine
Janine (a reference to the Simone package, from which Janine is a reload/remake), specially targeting GGM inference with underlying blockwise pattern governed by an SBM. The inference alternate adaptive graphical-LASSO and SBM with variational EM. The weigths in the graphical-Lasso are
where \(\hat{\mathcal{G}}\) is the current estimate of the network and \(\hat{\mathbb{P}}(i \leftrightarrow j)\) is the estimated probability of connection between any dyad under the fitted SBM (that is, conditional on the block of the nodes).
The overall amount of sparsity is tuned by the argument penalties, and the number of blocks in the SBM is fixed by argument n_blocks. By default, janine is fitted on a vector of penalties automaticcaly generated.
par(mfrow = c(1,2)) corrplot(as_adj(myMBM, sparse = FALSE), method = "color", is.corr=FALSE, tl.cex = .5, cl.pos = "n", type = "upper", tl.pos = 'n') plot(fits$models[[1]], type = "support") title(main= "\n True vs estimated graph", outer = TRUE)